Science
The infrared optimised JWST will give new insights on some of the hottest topics in modern Astronomy, such as:
- The end of the dark ages: First light and reionization
- Assembly of galaxies
- Birth of stars and protoplanetary systems
- Planetary systems and the origin of life
Observation Programs
JWST is scheduled for launch in March 2021. Science observations will commence after a 6 month commissioning phase, with Cycle 1 proposals deadline TBD.
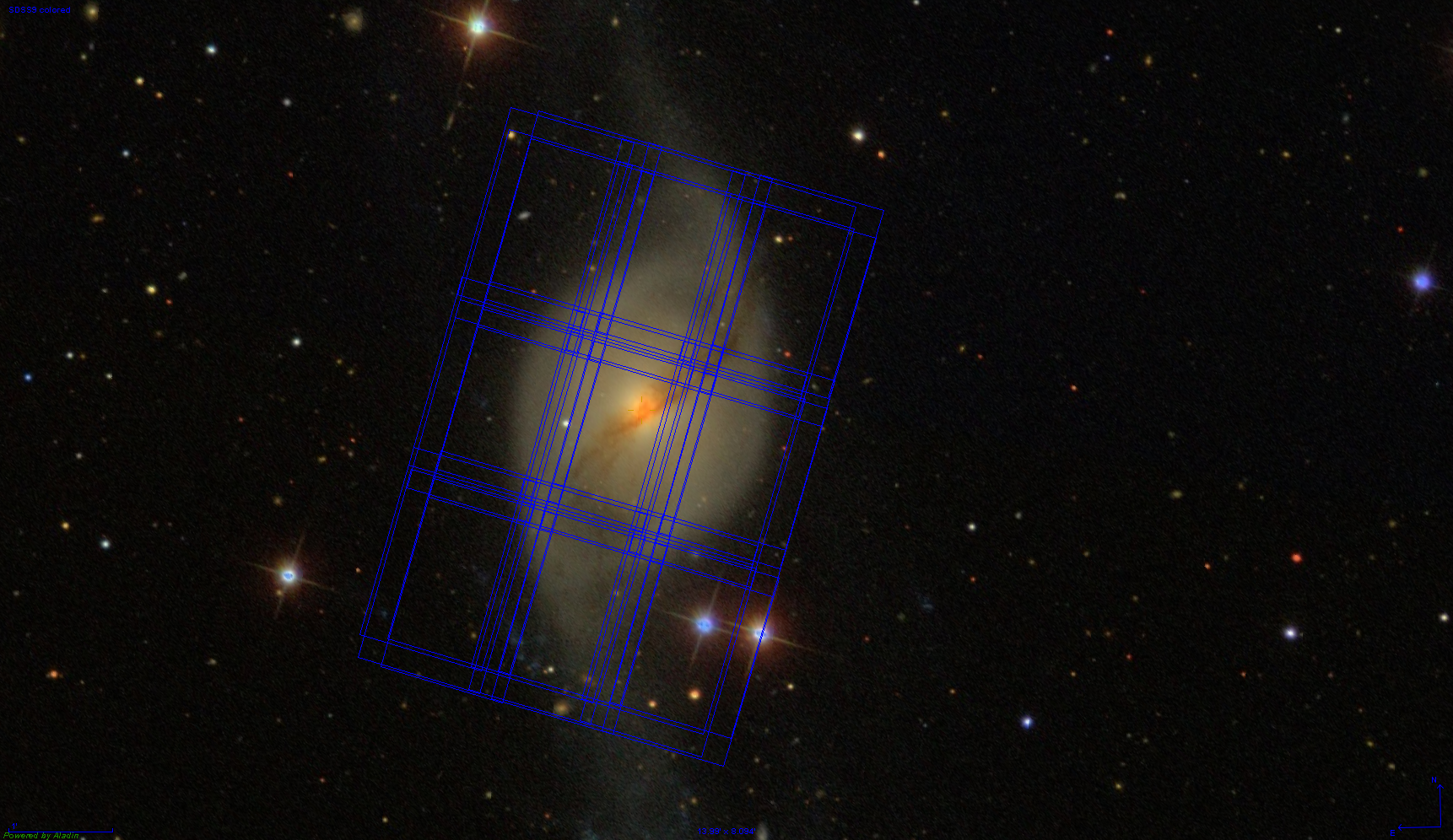
The unique capabilities of JWST will allow for a large-scale mapping of nearby galaxies covering a wide wavelength
range in the near- and mid-infrared that offers many important diagnostics and is widely uncharted territory.
Furthermore, the integral-field units deliver spatially resolved spectroscopy of the nucleus with unprecedented
spatial resolution.
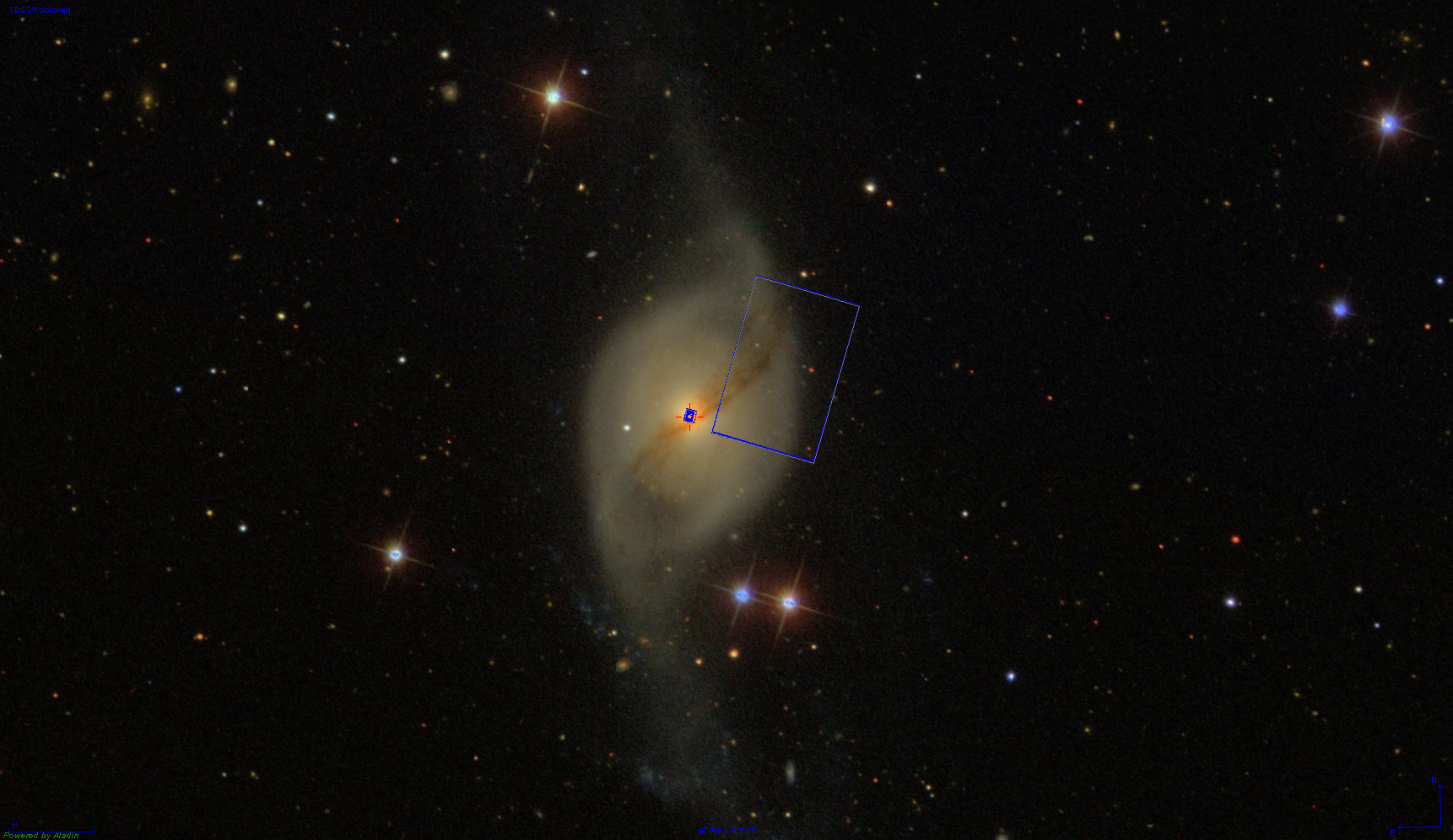
NGC 3718 is an extremely promising candidate for hosting a recoiled Super-Massive Black Hole (SMBH). The phenomenon of recoiled SMBHs offers deep implications for the Unified Model of AGN and the understanding of galaxy and SMBH
interaction and merging. The topic has only become accessible in the last few years thanks to breakthroughs in
numerical relativity allowing full simulations of merging black holes. In the near future, the combination of
electromagnetic and gravitational wave observations will offer further fascinating insights.
The nuclei of galaxies and their immediate vicinity are unique laboratories for a number of complex physical processes. JWST and MIRI will provide access to a multitude of diagnostic features of the Galactic Center.